Steric and electronic modulation of iron catalysts as a route to remarkably high molecular weight linear polyethylenes†
Abstract
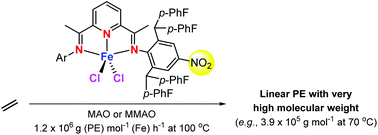
Five structurally related bis(arylimino)pyridine-iron(II) chloride complexes, [2-[CMeN{2,6-{(4-FC6H4)2CH}2-4-NO2}]-6-(CMeNAr)C5H3N]FeCl2 (Ar = 2,6-Me2C6H3Fe1, 2,6-Et2C6H3Fe2, 2,6-i-Pr2C6H3Fe3, 2,4,6-Me3C6H2Fe4, and 2,6-Et2-4-MeC6H2Fe5), incorporating one N-2,6-bis{di(4-fluorophenyl)methyl}-4-nitrophenyl group and one distinct N-aryl group, have been prepared in good yield through the interaction of the corresponding free ligands (L1–L5) with FeCl2·4H2O. All ferrous complexes were paramagnetic which was manifested by broad and highly shifted peaks in their 1H NMR spectra. The marked steric imbalance imposed by the two inequivalent N-aryl groups was a key feature highlighted in the molecular structures of representative complexes Fe1 and Fe2. Upon activation with either MAO or MMAO, Fe1–Fe5 all exhibited high activities for ethylene polymerization with good thermal stability [activities as high as 1.58 × 107 g (PE) mol−1 (Fe) h−1 at 60 °C], affording especially high molecular weight linear polyethylenes (3.92 × 105 g mol−1 at 70 °C; Tm > 130 °C). To the best of our knowledge, the molecular weights of the polyethylenes produced by the current class of iron catalysts exceed the highest values reported for related bis(imino)pyridine-iron catalysts to date; changes in the ortho-R1 substitution pattern offered some additional fine control of the molecular weight. Moreover, the nature of the aluminoxane co-catalyst employed had a noticeable effect on the polymer end group composition. When using MAO, unsaturated polymers containing both vinyl and n-propyl end groups were evident, whereas with MMAO, fully saturated polymers were generated containing both isobutyl and n-propyl end groups.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...