Three peroxidovanadium(v) compounds mediated by transition metal cations for enhanced anticancer activity†
Abstract
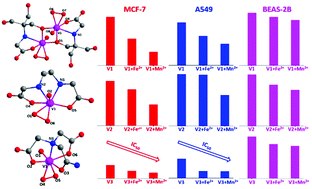
Three peroxidovanadium(V) compounds with different ligands (L1–L3) {L1 = N-tris(hydroxymethyl)methylglycine; L2 = ethylenediamine-N,N′-diacetic acid; L3 = 2,2-[(2-amino-2-oxoethyl)imino]diacetic acid} were first synthesized, characterized and further investigated for their anticancer activities under the mediation of transition metal cations. Encouragingly, all compounds showed preferentially enhanced cytotoxicity toward cancer cells (MCF-7 and A549) compared to normal cells (BEAS-2B) under the mediation of transition metal cations (Mn2+ or Fe2+), especially for Mn2+. It was noted that cell death was triggered by the transition metal cation-mediated peroxidovanadium(V) compounds through the induction of early apoptosis, inhibition of cell cycles, and boosting the generation of intracellular reactive oxygen species (ROS). Mechanistic studies further elucidated the vital roles of an acidic environment and transition metal cations for the anticancer activity of peroxidovanadium(V) compounds. Therefore, this study will offer precious insight into the development of the transition metal cation-mediated peroxidovanadium(V) compounds for further clinical translation.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...