Neutral nano-polygons with ultrashort Be–Be distances†
Abstract
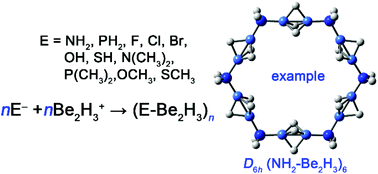
Ultrashort metal–metal distances (USMMDs, dM–M < 1.900 Å) have been realized computationally between the main group metal beryllium. However, due to their ionic charge state and the insufficient stability of their electronic structures and/or thermodynamic stabilities, the known species with ultrashort Be–Be distances are unsuitable for synthesis in the condensed phase, which deters the applications of these interesting structures from being explored. In the present study, using our previously reported global minima species [XH3–Be2H3–XH3]+ (X = N and P) with ultrashort Be–Be distances and well-defined electronic structures as their parent molecules, we designed a series of neutral polygons retaining ultrashort Be–Be distances. These polygons also possess well-defined electronic structures and good thermodynamic stabilities, which are demonstrated by their large HOMO–LUMO gaps of 6.20–7.68 eV, very high vertical detachment energies (VDEs) of 8.96–11.29 eV, rather low vertical electron affinities (VEAs) of −1.21 to +1.78 eV, and unexpectedly high formation energies relative to the building blocks of E− and Be2H3+ (−105.2 to −153.2 kcal mol−1 for the formation of an E–Be bond). The good stability with regard to their electronic structures and thermochemistry reveal their high feasibility to be synthesized in the condensed phase. Thus, we anticipate experimental studies on these interesting nano-polygons to realize structures with USMMDs between main group metals and explore their possible application.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...