Investigation of the structural, optical and electrical properties of Ca2+ doped CuCoO2 nanosheets†
Abstract
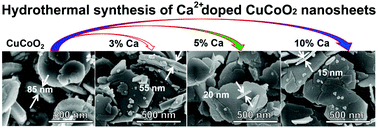
In this work, we present the hydrothermal synthesis of delafossite oxide Ca-doped CuCoO2 (CCCaO) nanosheets at a low temperature of 100 °C. The crystal phase, morphology and chemical composition of these CuCoO2 (CCO) based samples were comprehensively characterized by powder X-ray diffraction (XRD), field-emission scanning electron microscopy (FESEM), transmission electron microscopy (TEM), X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS), and Raman spectroscopy. The size of CCCaO nanosheets decreased with increasing Ca dopant concentration, and the optimized CCCaO nanosheets (∼490 nm in lateral size and ∼15 nm in thickness) were much smaller than CCO nanocrystals (∼540 nm in lateral size and 85 nm in thickness). The specific surface area of these CCO based samples increased with increasing Ca content, and the optimized CCCaO nanosheets present a high BET surface area of 28 m2 g−1. XPS and Raman spectroscopy analyses indicate Ca2+ dopant substitution on the Cu+ site in CCCaO nanosheets. Moreover, the effects of Ca2+ doping on the optical and electrical properties of these CCO based samples were further studied. The optical properties measured at room temperature show high absorbability (up to 90%) in the ultraviolet-visible-near infrared (UV-VIS-NIR) region, and the indirect band gap shows a significant blue-shift with increasing Ca2+ concentration. The CCO nanocrystals possess a higher electrical conductivity than the CCCaO nanosheets, and present good conductivities of around 12.81, 4.47 and 0.69 s m−1 for the CCO and CCCaO samples at room temperature. The facile fabrication process, tunable crystallite sizes, and excellent optical absorption and electrical properties of these CCO based nanomaterials are encouraging for the development of future applications in photoelectric devices.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...