An integrating photoanode consisting of BiVO4, rGO and LDH for photoelectrochemical water splitting
Abstract
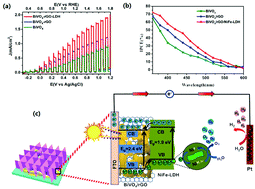
The low carrier mobility of BiVO4 is a bottleneck that limits its charge transfer in bulk or on the surface. Herein, reduced graphene oxide (rGO) nanosheets as an effective electron mediator were successfully loaded on BiVO4 and NiFe-layered double hydroxides (NiFe-LDHs) were decorated on BiVO4/rGO heterojunctions by two facile electrodeposition methods to construct a triadic photoanode of BiVO4/rGO/NiFe-LDH for improvement of photoelectrochemical (PEC) water splitting efficiency of BiVO4. This photoanode significantly extends the absorption region of visible light, increases the photocurrent density, exhibits an onset potential with a significant cathodic shift, and enhances photon-to-electron conversion efficiency (IPCE) compared with the pristine BiVO4 photoanode. The enhancement of PEC properties benefits from the formation of p–n heterojunctions between rGO and BiVO4 and the use of NiFe-LDH as a cocatalyst for accelerating the kinetics of oxygen evolution from water.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...