Cobalt amino-bis(phenolate) complexes for coupling and copolymerization of epoxides with carbon dioxide†
Abstract
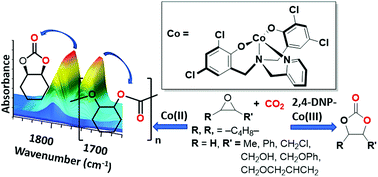
Cobalt(II) and (III) complexes bearing tetradentate amino-bis(phenolate) ligands containing either pendent dimethylaminoethylene or pyridyl groups and phenolates bearing electron-donating alkyl or electron-withdrawing chloro substituents were synthesized. The compounds were characterized by mass spectrometry, elemental analysis and NMR for diamagnetic compounds. The influence of the electron donating ability and steric demand of the ligands on CO2/epoxide ring-opening copolymerization (ROCOP) and coupling reactions was investigated. Of the Co(II) systems studied, complex 3, which has an amino-bis(phenolate) ligand possessing chlorine-functionalized phenolates and a pyridyl pendent group, [L3] = 2-methylene-pyridyl-N,N-bis(2-methylene-2,4-dichlorophenolate), was active for poly(cyclohexene carbonate) formation. The complex showed up to 98% epoxide conversion, up to 98% polymer selectivity and up to 97% carbonate linkages. By comparison, Co(II) compounds 1 and 2 bearing alkyl groups on the phenolate donors were inactive for ROCOP. Structural characterization of 3 by X-ray diffraction (and supported by mass spectrometry and elemental analysis) showed the potassium acetate (KOAc), which formed as a synthetic by-product, remains coordinated to the Co[L3] unit through binding of the K+ ions to the chlorine substituents on the phenolate groups and acetate anions, resulting in a hexacobalt cluster in the solid state. Cobalt(III) compounds were prepared from the Co(II) complexes by aerobic oxidation in the presence of 2,4-dinitrophenol. The resulting 2,4-dinitrophenolate (2,4-DNP) complexes were diamagnetic species of which 7, possessing a dimethylamino-N,N-bis(2-methylene-2-tert-butyl-4-methyl-phenolate) ligand [L4], was characterized by single crystal X-ray diffraction. The Co(III) complexes 5–7 were inactive for ROCOP of cyclohexene oxide or propylene oxide but were active for cyclic carbonate formation for a variety of epoxides studied. A maximum turnover frequency of 20 h−1 was attained for conversion of epichlorohydrin to (chloromethyl)ethylene carbonate.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...