Benzothiazole integrated into a cryptand for ESIPT-based selective chemosensor for Zn2+ ions†
Abstract
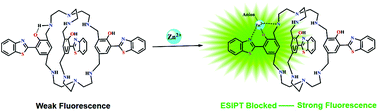
A novel benzothiazole-based cryptand was designed and synthesized, and it exhibited high fluorescence intensity in the presence of Zn2+ ions based on the metal chelation inhibition of the excited state intramolecular proton transfer (ESIPT) process. The structure of the cryptand was confirmed by NMR, mass spectroscopy and X-ray crystallography. Importantly, this probe showed high selectivity over other biologically relevant metal ions and anions and a detection limit of 0.20 μM, which is acceptable within the EPA (US) limit.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...