A portable oligonucleotide-based microfluidic device for the detection of VEGF165 in a three-step suspended-droplet mode†
Abstract
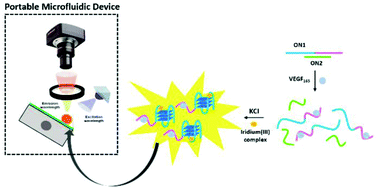
Vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF165), an important glycosylated protein from the VEGF family, is a type of signal protein highly associated with the development and progression of cancers. In this work, we designed a G-quadruplex-based aptasensing platform for the sensitive and selective detection of VEGF165 in aqueous solution and red blood cell solution. A long-lived phosphorescence iridium(III) complex (1) with promising photophysical properties and a large Stokes shift was chosen as a selective G-quadruplex probe. The platform could achieve a limit of detection (LOD) down to the picomolar level using a conventional fluorometer. Furthermore, we successfully applied the platform to a three-step suspended droplet (SD)-based microfluidic device for the monitoring of VEGF165. In contrast to the channel-based and digital microfluidic chips, SD-based chips allow easy introduction of liquid samples, valve-free manipulation of multiple reaction steps and flexible volume range. Importantly, polypropylene (PP), a hydrophobic and thermally stable material, was chosen as a substrate to fabricate the chip for the SD-based microfluidic device. The PP-based chip allows the combination of superhydrophobic force, gravity and surface tension for effective driving of the suspended droplet throughout the channel without reverse migration. After assembling all the major components, including a UV lamp, a rotatable chip holder, a filter and a camera into the portable device, we successfully demonstrated the applicability of the device to detect VEGF165 in aqueous solution with a LOD of 0.33 nM at a signal-to-noise ratio (S/N) of 3 and a linear range of 1–100 nM.
- This article is part of the themed collection: The central role of the d-block metals in the periodic table


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...