Synthesis, characterization and biological evaluation of cationic organoruthenium(ii) fluorene complexes: influence of the nature of the counteranion†
Abstract
In this study, five ruthenium arene complexes with fluorene-bearing N,N-(1) and N,O-(2) donor Schiff base ligands were synthesized and fully characterized. Cationic ruthenium complexes 3[X], ([Ru(η6-C6H6)(Cl)(fluorene-N![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) CH-pyridine)][X] (where X = BF4, PF6, BPh4), were obtained by reacting ligand 1 with [Ru(η6-C6H6)Cl2]2 in the presence of NH4X salts, whereas neutral complex 4, Ru(η6-C6H6)(Cl)(fluorene-N
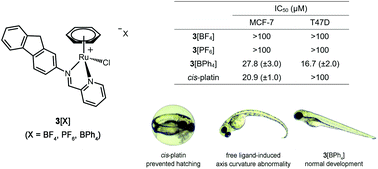
CH-pyridine)][X] (where X = BF4, PF6, BPh4), were obtained by reacting ligand 1 with [Ru(η6-C6H6)Cl2]2 in the presence of NH4X salts, whereas neutral complex 4, Ru(η6-C6H6)(Cl)(fluorene-N![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) CH-naphtholate), was isolated by reacting ligand 2 with the same precursor. It was possible to obtain a cationic version of the latter, 5[BF4], by reacting 4 with AgBF4 in the presence of pyridine. All compounds were fully characterized by NMR and HR-ESI-MS whereas some of them were also analyzed by single crystal X-ray analysis. Their in vitro antiproliferative activity was also assessed in human breast cancer cell lines, notably MCF-7 and T47D. Complex 4 and its cationic counterpart 5[BF4] were found to be the most cytotoxic compounds of the series (IC50 = 6.2–16.2 μM) and displayed higher antiproliferative activities than cisplatin in both cell lines. It was found that 5[BF4] undergoes a ligand exchange reaction and readily converts to 4 in the presence of 0.1 M NaCl, explaining the similarity in their observed cytotoxicities. Whereas 3[BF4] and 3[PF6] were found inactive at the tested concentrations, 3[BPh4] displayed a considerable cytotoxicity (IC50 = 16.7–27.8 μM). Notably, 3[BPh4], 4 (and 5[BF4]) were active against T47D, a cisplatin resistant cell line. Interestingly, 4 (16.4 μM) was found to be less cytotoxic than 3[BPh4] and cisplatin (6.6 and 7.9 μM, respectively) in breast healthy cells (MCF-12A). However, in comparison to 4 and cisplatin (at 10 μM), a lower in vivo toxicity was observed for complex 3[BPh4] on the development of zebrafish (Danio rerio) embryos.
CH-naphtholate), was isolated by reacting ligand 2 with the same precursor. It was possible to obtain a cationic version of the latter, 5[BF4], by reacting 4 with AgBF4 in the presence of pyridine. All compounds were fully characterized by NMR and HR-ESI-MS whereas some of them were also analyzed by single crystal X-ray analysis. Their in vitro antiproliferative activity was also assessed in human breast cancer cell lines, notably MCF-7 and T47D. Complex 4 and its cationic counterpart 5[BF4] were found to be the most cytotoxic compounds of the series (IC50 = 6.2–16.2 μM) and displayed higher antiproliferative activities than cisplatin in both cell lines. It was found that 5[BF4] undergoes a ligand exchange reaction and readily converts to 4 in the presence of 0.1 M NaCl, explaining the similarity in their observed cytotoxicities. Whereas 3[BF4] and 3[PF6] were found inactive at the tested concentrations, 3[BPh4] displayed a considerable cytotoxicity (IC50 = 16.7–27.8 μM). Notably, 3[BPh4], 4 (and 5[BF4]) were active against T47D, a cisplatin resistant cell line. Interestingly, 4 (16.4 μM) was found to be less cytotoxic than 3[BPh4] and cisplatin (6.6 and 7.9 μM, respectively) in breast healthy cells (MCF-12A). However, in comparison to 4 and cisplatin (at 10 μM), a lower in vivo toxicity was observed for complex 3[BPh4] on the development of zebrafish (Danio rerio) embryos.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...