Diiron(ii) pentacarbonyl complexes as CO-releasing molecules: their synthesis, characterization, CO-releasing behaviour and biocompatibility†
Abstract
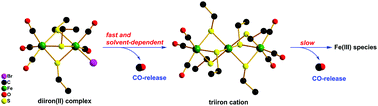
Four diiron(II) carbonyl complexes, [Fe2(μ-SR)3(CO)5X] (X− = Br−, I−; R = CH2CH3, CH2CH2CH3) were facilely synthesized by reacting [Fe(CO)4X2] with monothiolates. Their potential as carbon monoxide-releasing molecules (CORMs) was systematically investigated, revealing that their CO-releasing behaviour is highly solvent-dependent. Specifically, in dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO), the CO-releasing kinetics were fast. Intermediates with a lower oxidation state might be involved in the reaction. By contrast, in less polar solvents such as methanol, acetonitrile and dichloromethane, intermediates featuring the triiron carbonyl cation, [Fe3(μ-SCH2CH3)6(CO)6]+, were isolated. The triiron intermediate underwent further decomposition to liberate CO. One of the iodo complexes was also examined for its CO-release in PBS solution when solubilised with DMSO in the presence of deoxy-Mb and the CO-release was found to be quantitative. Furthermore, kinetic analyses were performed and the CO-release in general obeyed a first-order kinetic model. Plausible CO-releasing pathways are proposed for the parent complexes and the triiron intermediate. Assessments in cytotoxicity indicated that the cytoxicity of the diiron(II) complexes varied with both the halide and thiolate and those bearing bromide and the thiolate with longer chains were more biocompatible.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...