Photodegradation of volatile organic compounds catalyzed by MCr-LDHs and hybrid MO@MCr-LDHs (M = Co, Ni, Cu, Zn): the comparison of activity, kinetics and photocatalytic mechanism†
Abstract
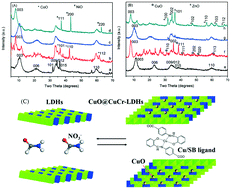
The efficient removal of high-concentration volatile organic compounds (VOCs) has been a challenging task. Here, four types of organic-inorganic hybrid layered double hydroxides (MO@MCr-LDHs, M = Co, Ni, Cu, Zn) were synthesized and used for highly efficient photodegradation of p-xylene under visible-light irradiation. The reactivity of the four hybrid MO@MCr-LDHs was found to follow the following general order: CuO@CuCr-LDHs CuCr-LDHs > ZnO@ZnCr-LDHs > NiO@NiCr-LDHs > CoO@CoCr-LDHs. Under the optimized reaction conditions (2.0 g catalyst dosage, 500 W, 50% relative humidity, 40 °C), >87% of p-xylene was removed by hybrid CuO@CuCr-LDHs after a 180 min reaction (from 175 mg m−3 to 22.6 mg m−3), which was triple the reactivity of MCr-LDHs. By comparing the physiochemical structures of the catalysts, we found that the hybridization of MO and MCr narrows the band gap (from 2.84 to 2.29 eV), increases the specific surface area (from 69.5 m2 g−1 to 139.1 m2 g−1) of LDHs, and enhances the photocatalytic property for VOC degradation (including benzene, toluene, o-xylene, and m-xylene), thus leading to more efficient generation of reactive species, decrease in the apparent activation energy, improvement in the electrochemical property, and possible changes in the reaction intermediates and pathways.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...