Upgrading of furfural to biofuel precursors via aldol condensation with acetone over magnesium hydroxide fluorides MgF2−x(OH)x†
Abstract
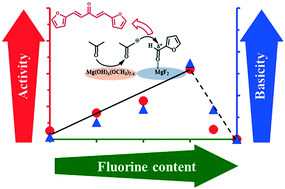
Wastes from lignocellulosic materials, especially hemicellulose, are extremely promising resources to produce fuels from renewable raw materials. Furfural, resulting from the depolymerization of hemicellulose, is often considered as an extremely interesting platform molecule. Particularly, new biofuels containing molecules with 8 and 13 carbon atoms can be produced from aldol condensation of furfural and acetone followed by a deoxygenation reaction. In this work, several magnesium hydroxide fluorides MgF2−x(OH)x were prepared by a sol–gel method with various F/Mg ratios (0 to 2) at 100 °C. All solid samples were fully characterized by several techniques (nitrogen adsorption–desorption, TEM, IR, XRD and ICP). MgF2−x(OH)x were mainly composed of an intimate mixture of MgF2 and Mg(OH)2−x(OCH3)x and exhibited both acid–base properties and high surface areas. From CO2 adsorption experiments, a basicity scale corresponding to basic sites with moderate strength was established: MgF1.5(OH)0.5 > MgF(OH) ∼ MgF1.75(OH)0.25 > MgF0.5(OH)1.5 > Mg(OH)2 ≫ MgF2. It was proposed that the presence of fluorine allowed stabilization of the basic sites with moderate strength at ambient atmosphere. The aldol condensation of furfural and acetone was carried out under mild reaction conditions (50 °C, Patm) over MgF2−x(OH)x. These catalysts were involved in this reaction without using a classical activation step for basic solid catalysts, which constitutes a major advantage of energy conservation and thus, economic efficiency. The solid with a F/Mg ratio equal to 1.5 (MgF1.5(OH)0.5) exhibited the highest activity, the furanic dimer (1,5-di(furan-2-yl)penta-1,4-dien-3-one) being the main product. A good correlation between the catalytic activity and the basicity scale was highlighted. Based on these results, the nature of active sites was proposed: a combination of a Lewis acid site (coordinatively unsaturated metal site) in the vicinity of a basic site (hydroxyl groups of Mg(OH)2−x(OCH3)x). The effect of the furfural/acetone ratio on the catalytic properties of MgF1.5(OH)0.5 was also investigated.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...