Effect of Ag–Fe–Cu tri-metal loading in bismuth oxybromide to develop a novel nanocomposite for the sunlight driven photocatalytic oxidation of alcohols†
Abstract
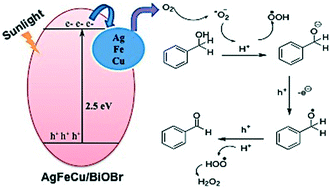
Metal (mono-, bi-, and tri-) doped BiOBr nanostructures were developed as sunlight driven reusable catalysts for the selective photocatalytic oxidation of alcohols. We describe a room temperature synthesis procedure for a series of different metal-doped BiOBr nanostructures, followed by the characterization of their compositions, crystallinity, and morphology by XPS, XRD, and SEM-EDAX. The materials were then applied as a photocatalyst for the selective oxidation of alcohols into corresponding aldehydes or ketones under sunlight. Initially, the activities of the materials were optimized by the photocatalytic oxidation of benzyl alcohols into benzaldehyde. The Ag–Fe–Cu tri-metal loaded BiOBr demonstrated an exceptional activity, which was much higher than those of mono- and bi-metal doped BiOBr. The reaction was carried out in the absence of any external oxygen source and completed within 1.5 h with a very high conversion efficiency (>99%) and selectivity (>99%). For generalization, the activity of the Ag–Fe–Cu tri-metal loaded BiOBr was extended to other alcohols (viz., substituted benzyl alcohols, phenyl ethyl alcohol, and 2-propanol), and found to maintain the activity with a similar selectivity and yield. However, the time for completion of the reaction differed slightly depending on the precursor alcohol. Next, scavenging experiments were carried out to establish a plausible mechanism for the reaction. Photogenerated holes and superoxide radicals were found to be mainly responsible for maintaining such a high selectivity. In addition, the as-synthesized metal-doped catalysts remained stable during the photocatalytic conversion process and could be repeatedly utilized, suggesting its potential in practical applications.
- This article is part of the themed collection: 2019 Catalysis Science & Technology HOT Articles


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...