An efficient, bifunctional catalyst for lithium–oxygen batteries obtained through tuning the exterior Co2+/Co3+ ratio of CoOx on N-doped carbon nanofibers†
Abstract
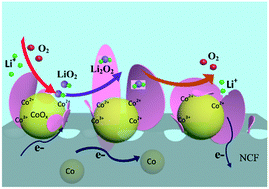
The design and fabrication of efficient catalysts are urgently desired for Li–O2 batteries to prompt both the oxygen reduction reaction and oxygen evolution reaction. Morphology/surface optimization can be intensively applied to enhance the catalytic activity of specific materials. Herein, we propose an electrospinning method followed by heat treatment to fabricate CoOx nanoparticles on N-doped carbon nanofibers (CoOx@NCF). Significantly, the electrocatalytic activity can be largely improved through modulating the exterior Co2+/Co3+ ratio by controlling the heat-treatment process. The prepared CoOx nanoparticles possess high uniformity together with good dispersion, which integrates the advantages of morphology and surface properties, making them an effective active catalyst for Li–O2 batteries. The cell with the CoOx@NCF catalyst shows impressively good performance towards the ORR and OER with a high initial discharge capacity (7763.7 mA h g−1), enhanced cycling stability, desirable rate capability and relatively low overpotential. Moreover, the result of LSV indicates that CoOx@NCF enables the decomposition of the side product LiOH efficiently. In addition, the CoOx@NCF catalyst is capable of forming nanosheet-like Li2O2, which is much easier to decompose, compared with toroidal-like Li2O2. The boosted cycling life can be attributed to the synergistic effect of architecture design and surface engineering.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...