Proton supplier role of binuclear gold complexes in promoting hydrofunctionalisation of nonactivated alkenes†
Abstract
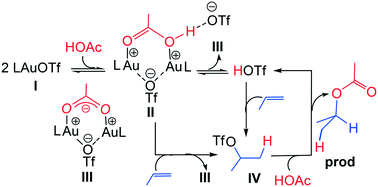
Density functional theory (DFT) was used to investigate PR3AuOTf-catalyzed hydrofunctionalisation of nonactivated alkenes using acetic acid and phenol where OTf = triflate (CF3SO3−). The gold(I) complex itself is found to be unlikely to operate as the π-activator due to its relatively low electrophilicity. Instead, the concurrent coordination of two gold(I) complexes to a nucleophile (PhOH or AcOH) enhances the acidity of the latter's proton and causes the ensuing binuclear complex to serve as a strong proton supplier for activating the alkene π-bonds. Alternatively, the binuclear complex is also susceptible to produce a hidden HOTf. This hidden acid is accessible for hydrofunctionalization to occur but it is not in sufficient concentration to decompose the final product.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...