On the ionic liquid films ‘pinned’ by core–shell structured Fe3O4@carbon nanoparticles and their tribological properties†
Abstract
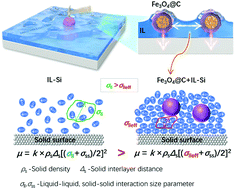
A strongly ‘pinned’ ionic liquid (IL, [BMIM][PF6]) film on a silicon (Si) surface via carbon capsuled Fe3O4 core–shell (Fe3O4@C) nanoparticles is achieved, revealing excellent friction-reducing ability at a high load. The adhesion force is measured to be ∼198 nN at the Fe3O4@C-Si interface by the Fe3O4@C colloidal AFM tip, which is stronger than that at both Fe3O4@C-Fe3O4@C (∼60 nN) and IL-Si (∼10 nN) interfaces, indicating a strong ‘normal pin-force’ towards the Si substrate. The resulting strengthened force enables the formation of lateral IL networks via the dipole–dipole attractions among Fe3O4 cores. The observed blue shift of the characteristic band related to the IL anion in the ATR-FTIR spectra confirmed the enhanced interaction. The N–Si, P–O chemical bonds formed as a result of the IL interactions with the Si substrate confirmed by XPS spectroscopy suggested that the IL lay on the Si plane. This orientation is favorable for Fe3O4@C nanoparticles to exert ‘normal pin-force’ and press the IL film strongly onto surfaces. The IL ions/clusters are thus anchored by these Fe3O4@C ‘pins’ onto the substrate to form a dense film, resulting in a smaller interaction size parameter, which is responsible for the reduced friction coefficient μ.
- This article is part of the themed collection: 2019 PCCP HOT Articles


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...