C2N/BlueP van der Waals hetero-structure: an efficient photocatalytic water splitting 2D material
Abstract
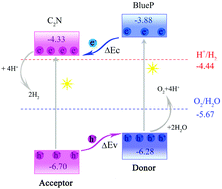
Constructing van der Waals (vdW) hetero-structures is an effective and feasible method to enhance two-dimensional (2D) materials with desired properties and to extend the application of the original materials. In this work, we establish a C2N/BlueP vdW hetero-structure and explore its photocatalytic water splitting performance by investigating the electronic structure, band edge alignment, charge transfer, optical absorption and strain response based on the density functional theory (DFT) method. Numerical results indicate that the C2N/BlueP hetero-structure possesses a proper direct bandgap and intrinsic type-II band alignment, which are beneficial to the space separation of photo-generated electron–hole pairs. The optical absorption of the hetero-structures is enhanced from the visible to ultraviolet light region compared with those of both individual monolayers. More importantly, the valence band maximum (VBM) is lower than the oxidation potential of water, and the conduction band minimum (CBM) is higher than the reduction potential of water, which indicates the proper photocatalytic potential for water splitting of the C2N/BlueP hetero-structure. By applying a small vertical pressure perpendicular to the hetero-structure with roughly 6% interlayer compression, both the band alignment and the optical absorption can be improved, which gives better performance of photocatalytic water splitting for the C2N/BlueP hetero-structure.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...