Ab initio insights into the structural, energetic, electronic, and stability properties of mixed CenZr15−nO30 nanoclusters†
Abstract
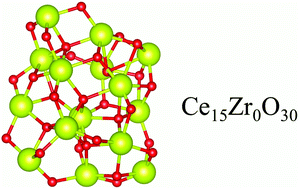
Mixed CeO2–ZrO2 nanoclusters have the potential to play a crucial role in nanocatalysis, however, the atomistic understanding of those nanoclusters is far from satisfactory. In this work, we report a density functional theory investigation combined with Spearman rank correlation analysis of the energetic, structural and electronic properties of mixed CenZr15−nO30 nanoclusters as a function of the composition (n = 0, 1,…,14, 15). For instance, we found a negative excess energy for all putative global minimum CenZr15−nO30 configurations with a minimum at about n = 6 (i.e., nearly 40% Ce), in which both the oxygen anion surroundings and cation radii play a crucial role in the stability and distribution of the chemical species. We found a strong energetic preference of Zr4+ cations to occupy larger coordination number sites, i.e., the nanocluster core region, while the Ce4+ cations are located near vacuum exposed O-rich regions. As expected, we obtained an almost linear decrease of the average bond lengths by replacing Ce4+ by Zr4+ cations in the (ZrO2)15 nanoclusters towards the formation of mixed CenZr15−nO30 nanoclusters, which resulted in a shift towards higher vibrational frequencies. Besides, we also observed that the relative stability of the mixed oxides is directly correlated with the increase (decrease) of the Zr d-state (Ce f-state) contribution to the highest occupied molecular orbital with the increase of the Zr content, hence driving the gap energy towards higher values.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...