Electronic structure of mono(Lewis base)-stabilized borylenes†
Abstract
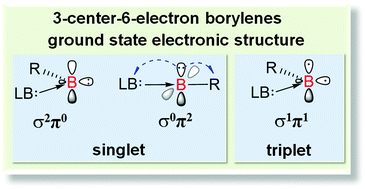
This work demonstrates that the mono(Lewis base)-stabilized three-center-six-electron (3c-6e) or LB → B–R type borylenes may have a ground state singlet (σ2π0 and σ0π2) or triplet (σ1π1) electronic structure, depending on the substitution group, Lewis base, and molecule topology (cyclic or acyclic). The singlet–triplet energy gap of a borylene increases with electron-donating substitution groups and decreases with Lewis bases of strong σ-donating and π-accepting feature (e.g., carbenes and pyridine). The gap can be widely varied (ranging up to about 300 kJ mol−1) and even inversed by the proper combination of substitution groups and Lewis bases. These borylenes may even have singlet-and-triplet coexisting ground state electronic structures, which imply their complex reactivity.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...