The influence of support materials on the structural and electronic properties of gold nanoparticles – a DFT study†‡
Abstract
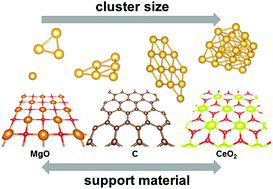
Supported gold nanoparticles are used for a wide range of catalytic processes. In this work, we use dispersion corrected density functional theory (DFT-D) to study the effect of commonly used support materials (MgO, C, CeO2) on small gold particles with up to 19 atoms. Our results show that the preferred cluster shape and morphology is highly dependent on the support material due to different adsorption strength and structural mismatch between the cluster and the surface material. We developed an algorithm to measure the mismatch between the cluster interface and the support surface. Moreover, depending on the support material, the gold clusters exhibit a positive or negative polarisation, which ultimately has strong implications on the catalytic activity of such particles. This behaviour is rationalised by an analysis of the electronic structure of the metal particles and support materials.
- This article is part of the themed collections: PCCP Editor’s Choice, 2020 and 2019 PCCP HOT Articles


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...