Plasmon-coupled 3D porous hotspot architecture for super-sensitive quantitative SERS sensing of toxic substances on real sample surfaces†
Abstract
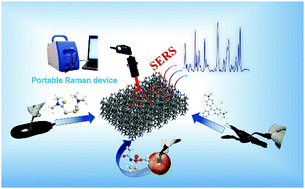
This paper reports a facile, fast, and cost-effective method for the synthesis of three-dimensional (3D) porous AgNPs/Cu composites as SERS substrates for the super-sensitive and quantitative detection of food organic contaminations. Due to the 3D porous hotspot architecture and the strong plasmonic coupling between Ag and Cu, the porous AgNPs/Cu substrate achieves ultrasensitive detection of multiple analytes as low as 10−11 M (crystal violet, CV), 10−9 M (malachite green, MG), 10−11 M (acephate), and 10−9 M (thiram) even with a portable Raman device. Moreover, this 3D solid substrate has good signal uniformity (RSD < 11%) and superior stability (<14% signal loss), allowing for practical SERS detections. Importantly, by simply wiping the real sample surface using the substrate, it successfully detects CV and MG residues on crayfish, and the limit of detection (LOD) of CV and MG is determined to be 1.14 × 10−9 M and 0.94 × 10−7 M, respectively. Further, the substrate can also be applied to detect acephate on eggplant with a LOD of 1.41 × 10−9 M and thiram on an apple surface with a LOD of 1.04 × 10−7 M. Note that all these SERS detections on real samples have a broad dynamic concentration range and a good linear dependence. As a “proof of concept”, multi-component detection on a real sample has also been demonstrated. This 3D solid substrate possesses excellent detection sensitivity, diversity, and accuracy, which allows rapid and reliable determination of toxic substances in foods.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...