Kerr gated Raman spectroscopy of LiPF6 salt and LiPF6-based organic carbonate electrolyte for Li-ion batteries†
Abstract
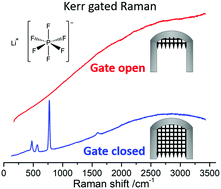
Fluorescent species are formed during cycling of lithium ion batteries as a result of electrolyte decomposition due to the instability of the non-aqueous electrolytes and side reactions that occur at the electrode surface. The increase in the background fluorescence due to the presence of these components makes it harder to analyse data due to the spectroscopic overlap of Raman scattering and fluorescence. Herein, Kerr gated Raman spectroscopy was shown to be an effective technique for the isolation of the scattering effect from the fluorescence enabling the collection of the Raman spectra of LiPF6 salt and LiPF6-based organic carbonate electrolyte, without the interference of the fluorescence component. Kerr gated Raman was able to identify POF3 on the LiPF6 particle surface, after the addition of trace water.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...