A C20-based 3D carbon allotrope with high thermal conductivity†
Abstract
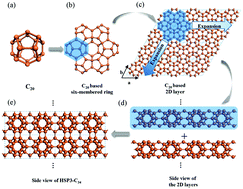
Stimulated by the high thermal conductivity of diamond together with the light mass and rich resources of carbon, a great deal of effort has been devoted to the study of the thermal conductivity of carbon-based materials. In this work, we systematically study the thermal transport properties of a three dimensional (3D) C20 fullerene-assembled carbon allotrope, HSP3-C34, in which all carbon atoms are in sp3 hybridization. The stability of HSP3-C34 is confirmed and its thermal conductivity is obtained by using first principles calculations combined with solving the linearized phonon Boltzmann transport equation. At room temperature, the thermal conductivity of HSP3-C34 is 731 W m−1 K−1, which is larger than those of many 3D carbon allotropes, such as BCO-C16 (452 W m−1 K−1), 3D graphene (150 W m−1 K−1) and T-carbon (33 W m−1 K−1). A detailed analysis of its phonons reveals that three acoustic branches are the main heat carriers at room temperature, and the optical branches gradually become important with increasing temperature. A further study on the harmonic and anharmonic properties of HSP3-C34 uncovers that the main reasons for the high thermal conductivity are the weak anharmonicity and large group velocity resulting from the strong sp3 bonding. This study provides new insights on searching for carbon allotropes with high thermal conductivity.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...