Resonance Raman study of the J-type aggregation process of a water soluble perylene bisimide†
Abstract
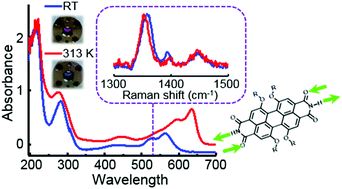
Perylene bisimides (PBIs) are dyes known for combining high absorption and emission in the visible region with thermal and photochemical stability. H-bond-directed aggregation driven by free imide groups has been reported to promote the uncommon J-type aggregate formation of PBIs. J-aggregates are highly desired thanks to their bathochromically shifted narrow absorption and fluorescence due to excitonic coupling, together with hyperchromicity and superradiance compared to the monomer. Herein we present the water soluble MEG-PBI showing interesting aggregation in water and in the solid state. Unlike its hydrophobic counterparts, MEG-PBI aggregates in water with increasing temperature, indicating entropy-driven self-assembly. Temperature-dependent Resonance Raman (RR) spectroscopy was employed for the structural characterization of MEG-PBI in aqueous solution versus toluene and in aggregated thin films, employing excitation at different wavelengths to probe the contribution of various chromophores to the supramolecular structure of the aggregate. We find that the perylene core distorts upon aggregation, where the bonds along the perylene long N–N axis lengthen and the ones perpendicular to that shorten, suggesting a head-to-tail arrangement due to H-bonding between neighboring units.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...