Organic salts utilising the hexamethylguanidinium cation: the influence of the anion on the structural, physical and thermal properties†
Abstract
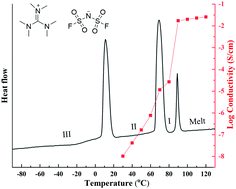
The synthesis and characterisation of new solid-state electrolytes is a key step in advancing the development of safer and more reliable electrochemical energy storage technologies. Organic ionic plastic crystals (OIPCs) are an increasingly promising class of material for application in devices such as lithium or sodium metal batteries as they can support high ionic conductivity, with good electrochemical and thermal stability. However, the choice of OIPC-forming ions is still relatively limited. Furthermore, understanding of the influence of different cations and anions on the thermal, structural and transport properties of these materials is still in its infancy. Here we report the synthesis and in-depth characterisation of a range of new OIPCs utilising the hexamethylguanidinium cation ([HMG]) with five different anions. The thermal, structural, transport properties and free volume in the different salts have been investigated. The free volume within the salts has been investigated by positron annihilation lifetime spectroscopy, and the single crystal and powder X-ray diffraction analysis of [HMG] bis(trifluoromethanesulfonyl)imide ([TFSI]) in phase I and II, [HMG] hexafluorophosphate ([PF6]) and [HMG] tetrafluoroborate ([HMG][BF4]) are reported. The HMG cation can exhibit significant disorder, which is advantageous for plasticity and future use of these materials as high ionic conductivity matrices. The bis(fluorosulfonyl)imide salt, [HMG][FSI], is identified as particularly promising for use as an electrolyte, with good electrochemical stability and soft mechanical properties. The findings introduce a range of new materials to the solid-state electrolyte arena, while the insights into the physico-chemical relationships in these materials will be of importance for the future development and understanding of other ionic electrolytes.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...