Reaction mechanism and kinetics for ammonia synthesis on the Fe(211) reconstructed surface†
Abstract
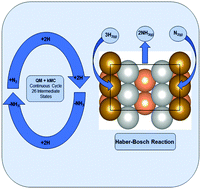
To provide guidelines to accelerate the Haber–Bosch (HB) process for synthesis of ammonia from hydrogen and nitrogen, we used Quantum Mechanics (QM) to determine the reaction mechanism and free energy reaction barriers under experimental reaction conditions (400 °C and 20 atm) for all 10 important surface reactions on the Fe(211) reconstructed (Fe(211)R) surface. These conditions were then used in full kMC modeling for 30 minutes to attain steady state. We find that the stable surface under Haber–Bosch conditions is the missing row 2 × 1 reconstructed surface (211)R and that the Turn Over Frequency (TOF) is 18.7 s−1 per 2 × 2 surface site for 1.5 Torr NH3 pressure, but changes to 3.5 s−1 for 1 atm, values close (within 6%) to the ones on Fe(111). The experimental ratio between (211) and (111) rates at low (undisclosed) NH3 pressure was reported to be 0.75. The excellent agreement with experiment on two very different surfaces and reaction mechanisms is a testament of the accuracy of QM modeling. In addition, our kinetic analysis indicates that Fe(211)R is more active than Fe(111) at high pressure, close to HB industrial conditions, and that (211)R is more abundant than (111) via a steady-state Wulff construction under HB conditions. Thus, at variance with common thinking, we advocate the Fe(211)R surface as the catalytically active phase of pure iron ammonia synthesis catalyst under HB industrial conditions.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...