Viscoelastic micellar solution formed by a Se-based ionic liquid surfactant and its response to redox changes†
Abstract
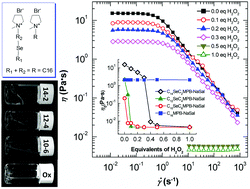
Redox-responsive colloidal systems based on selenium-containing molecules have recently attracted considerable attention. However, the effects of a Se atom and its site in a hydrophobic chain are yet to be fully characterized. In this study, we synthesized three ionic liquid surfactants with similar molecular structures (CmSeCnMPB, m = 14, 12, and 10, n = 2, 4, and 6), in which the spacers between the Se atom and the polar headgroup comprise 2, 4, and 6 CH2 units, respectively. Their abilities to form worm-like micelles (WLMs) in the presence of sodium salicylate (NaSal) were investigated and compared to that of N-cetyl-N-methylpyrrolidinium bromide (C16MPB) with no Se atom in its hydrophobic chain. The results showed that the incorporation of a Se atom endows the molecules with redox-sensitivity, and that its site also plays a crucial role. In the presence of NaSal, all CmSeCnMPB analogues self-assemble into viscoelastic WLMs. The viscosity enhancing abilities of the compounds followed an order of C14SeC2MPB-NaSal > C12SeC4MPB-NaSal ≈ C16MPB-NaSal > C10SeC6MPB-NaSal, coinciding with the variation trend of micelle formation in one-component CmSeCnMPB solutions. Upon the addition of H2O2, the selenide was oxidized to selenoxide, enhancing the hydrophilicity and changing the molecular structure, and thus the viscoelastic WLM network was disrupted. Due to the different geometry adopted after oxidation, the critical concentration of H2O2 that was required to induce the gel-to-sol transition was also distinct. Only 0.1 equiv. of H2O2 was required for C12SeC4MPB-NaSal or C10SeC6MPB-NaSal, but 0.4 equiv. of H2O2 was required for C14SeC2MPB-NaSal. These viscoelastic fluids represent good candidates for drug delivery.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...