Unexpected chalcogen bonds in tetravalent sulfur compounds†
Abstract
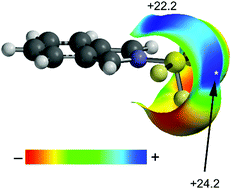
In this manuscript we have combined a CSD (Cambridge Structural Database) analysis with theoretical calculations (RI-MP2/def2-TZVP level of theory) to study the importance of polarizability in chalcogen bonding interactions. It is well known that chalcogen bonds are stronger for less electronegative chalcogen atoms, i.e., S < Se < Te, and in the presence of electron-withdrawing substituents at the chalcogen. Herein, we report experimental and theoretical evidence (RI-MP2/def2-TZVP) that the chalcogen bond acceptor (Lewis base) has a preference in some cases for the σ-hole that is opposite to the more polarizable group instead of the more electron withdrawing one, as confirmed by Natural Bond Orbital (NBO) and Bader's theory of “atoms-in-molecules” computational tools.
- This article is part of the themed collection: 1st International Conference on Noncovalent Interactions


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...