Adsorption, surface relaxation and electrolyte structure at Pt(111) electrodes in non-aqueous and aqueous acetonitrile electrolytes†
Abstract
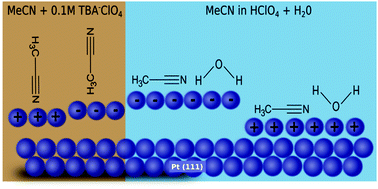
In situ electrochemical surface X-ray diffraction was employed to investigate the atomic scale structure of the electrochemical double layer and the relaxation at the Pt(111) electrode surface in non-aqueous and aqueous acetonitrile electrolytes under potential control. The X-ray measurements provide insight into the potential-dependence of the interface structure by combining potentiodynamic measurements (X-ray voltammetry) with potentiostatic measurements (crystal truncation rod data) to probe both the metal and electrolyte sides of the interface. The crystal truncation rod measurements are consistent with the potential dependent reorientation of acetonitrile in the absence of water and a parallel arrangement in the presence of water. As acetonitrile concentration increases, the electron density closest to the electrode surface also increases. Finally, Pt surface relaxation in a range of aqueous and non-aqueous solvents is discussed in general with regards to the structure of the electrochemical double layer.
- This article is part of the themed collection: 2019 PCCP HOT Articles


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...