Capturing a dynamically interacting inhibitor by paramagnetic NMR spectroscopy†
Abstract
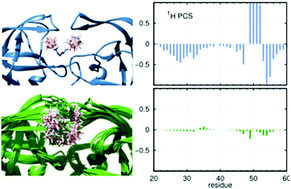
Transient and fuzzy intermolecular interactions are fundamental to many biological processes. Despite their importance, they are notoriously challenging to characterize. Effects induced by paramagnetic ligands in the NMR spectra of interacting biomolecules provide an opportunity to amplify subtle manifestations of weak intermolecular interactions observed for diamagnetic ligands. Here, we present an approach to characterizing dynamic interactions between a partially flexible dimeric protein, HIV-1 protease, and a metallacarborane-based ligand, a system for which data obtained by standard NMR approaches do not enable detailed structural interpretation. We show that for the case where the experimental data are significantly averaged to values close to zero the standard fitting of pseudocontact shifts cannot provide reliable structural information. We based our approach on generating a large ensemble of full atomic models, for which the experimental data can be predicted, ensemble averaged and finally compared to the experiment. We demonstrate that a combination of paramagnetic NMR experiments, quantum chemical calculations, and molecular dynamics simulations offers a route towards structural characterization of dynamic protein–ligand complexes.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...