Is it possible for short peptide composed of positively- and negatively-charged “hydrophilic” amino acid residue-clusters to form metastable “hydrophobic” packing?†
Abstract
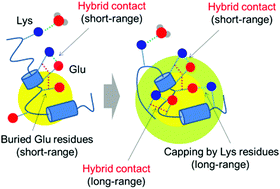
We theoretically and experimentally analyzed a conformational ensemble of a small, characteristic polypeptide consisting of positively- and negatively-charged amino acid residue clusters, (Lys)9(Glu)9(Lys)9, designed based on the supercoiled DNA-recognition (SDR) domain, with the capability of preferentially binding to supercoiled DNA. Advanced molecular dynamics (MD) simulations coupled with a generalized ensemble technique revealed that substantial amounts of ordered, helical structures were present at the boundaries of the Lys and Glu segments in the obtained conformational ensemble. In fact, the helical content of the peptide calculated from our MD simulations was consistent with that estimated from our experimental analysis employing circular dichroism (CD) spectroscopy. The statistical analysis of the structural ensemble revealed the metastable hydrophobic contact clusters, which were stabilized by closely cohesive residue contacts, formed through “hybrid” hydrophobic (methylene groups) and electrostatic (salt bridges) residue contacts. Both short-range and long-range residue contacts were involved in the metastable hydrophobic clusters, constituting the aforementioned local helical conformations and the compact entire structures, respectively. A significant helical propensity was also found in the (Lys)n and (Glu)m boundaries of other conventional protein structures deposited in the Protein Data Bank (PDB), thus indicating the generality of this conformational trend that has been identified herein.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...