Activation of CO2 at the electrode–electrolyte interface by a co-adsorbed cation and an electric field†
Abstract
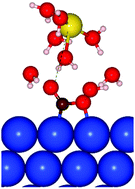
Carboxylate *CO2− has recently been identified as the first intermediate of the CO2 electroreduction independent of the reaction pathway. However, on the fundamental level, the structural and electronic properties of *CO2− remain poorly understood especially under the electrocatalytic conditions, which limits our capacity to rationally control the transformation of this reaction intermediate to CO or formate. To close this gap, we model using density functional theory (DFT) the interactions of *CO2− with the copper Cu(111) surface and a co-adsorbed sodium cation in the electric double layer (EDL), as well as the effects of electrode potential on these interactions. We demonstrate that *CO2− is activated by a co-adsorbed alkali cation most strongly when it forms with the cation a noncovalent bond (ion pair), where the cation is coordinated in the on-top position. The most stable structure of this ion pair with a sodium cation is hydration-shared. An external negative electric field not only enhances activation of *CO2− but also tilts it in the *CO2− plane, elongating the metal–C bond and contracting the metal–O bond. This tilting facilitates hydrogenation of the C atom and dissociation of the surface-coordinated C–O bond. Based on a detailed analysis of the projected density of states (pDOS), we interpret these findings in terms of electrostatic and chemical effects. The provided insights can help understand the relationship between properties of the catalytic system and its catalytic activity in the CO2 conversion to CO and formate, and hence help develop new CO2 electroreduction catalysts.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...