Mechanisms of phase separation in temperature-responsive acidic aqueous biphasic systems†
Abstract
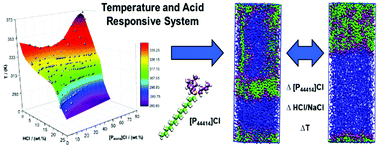
The temperature responsive solubility of ionic liquids with ‘bulky’ polar regions, such as tributyltetradecyl phosphonium chloride ([P44414]Cl), in acidic aqueous solutions is elucidated through a combined experimental and computational approach. The temperature effect in the acidic aqueous biphasic system HCl/[P44414]Cl/H2O was characterised in the range 273 K to 373 K and was found to significantly deviate from the corresponding aqueous biphasic system with NaCl. A new transferable coarse grained MARTINI model for [P44414]Cl was developed, validated and applied to provide a molecular understanding of the experimental results. It is shown that the presence of large aliphatic moieties around the central phosphorus atoms of [P44414]Cl results in a decrease in the electrostatic repulsion between the cationic moieties, leading the [P44414]+ cation to present a behaviour conventionally associated with non-ionic surfactants. This difference in behaviour between HCl and NaCl was shown to result from the greater interaction of the hydronium cation with the micelle surface, thereby enhancing the [P44414]Cl aggregation.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...