Reaction mechanism between small-sized Ce clusters and water molecules: an ab initio investigation on Cen + H2O†
Abstract
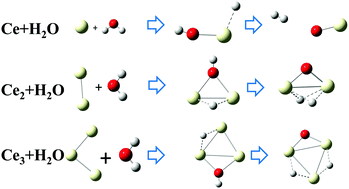
Reactions of small-sized cerium clusters Cen (n = 1–3) with a single water molecule are systematically investigated theoretically. The ground state structures of the Cen/H2O complex and the reaction pathways between Cen + H2O are predicted. Our results show the size-dependent reactivity of small-sized Ce clusters. The calculated reaction energies and reaction barriers indicate that the reactivity between Cen and water becomes higher with increasing cluster size. The predicted reaction pathways show that the single Ce atom and the Ce2 and Ce3 clusters can all easily react with H2O and dissociate the water molecule. Under UV-irradiation, the reaction of a Ce atom with a single H2O molecule may even release an H2 molecule. The reaction of either Ce2 or Ce3 with a single H2O molecule can fully dissociate the H2O into H and O atoms while it is bonded with the Ce cluster. The electronic configuration and oxidation states of the Ce atoms in the products and the higher occupied molecular orbitals are analyzed by using the natural bond orbital (NBO) analysis method, from which the high reactivity between the reaction products of Cen + H2O and an additional H2O molecule is predicted. Our results offer deeper molecular insights into the chemical reactivity of Ce, which could be helpful for developing more efficient Ce-doped or Ce-based catalysts.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...