Effects of the number of layers on the vibrational, electronic and optical properties of alpha lead oxide
Abstract
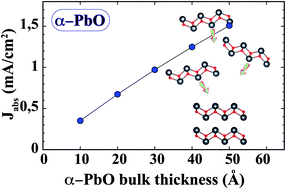
We have investigated the effects of the number of layers on the structure, vibrational, electronic and optical properties of α-PbO using first principles calculations. Our theoretical calculations have shown that four Raman active modes of α-PbO tend to red-shift from bulk to monolayer due to a decrease of the force constants and an increase of the bond lengths. It has been shown that while bulk and multilayer α-PbO have an indirect band gap, the monolayer form has a direct band gap value of 2.59 eV. Although lead atoms have 5d states, spin–orbit coupling does not significantly affect the band structure of α-PbO. The computed cleavage energy value (0.67 J m−2) confirms that monolayer PbO can be easily obtained from its bulk counterpart by exfoliation. In addition to the band structure, we also calculated the optical properties and absorbed photon flux Jabs of α-PbO structures to investigate the possibility of solar absorption. Our calculations reveal that while monolayer and bilayer PbO have relatively large band gaps and lower absorption coefficients, their Jabs values are not ideal for solar absorption devices. In contrast, the multilayer and bulk phases of the α-PbOs show good overlap with the solar spectrum and yield high electrical current values. Our calculations have indicated that ultrathin films of α-PbO (such as 3 nm thickness) could be excellent candidates for solar cells. We believe that our work can be utilized to improve electronic and optical devices based on lead oxide structures.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...