An experimental study of indene pyrolysis with synchrotron vacuum ultraviolet photoionization mass spectrometry†
Abstract
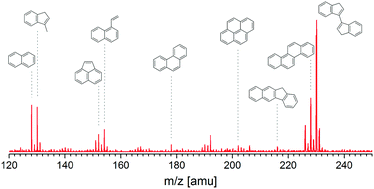
Pyrolytic kinetics of indene was studied in a flow reactor at 30 and 760 Torr. Indene and its decomposition products, as well as polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs), were measured with synchrotron vacuum ultraviolet photoionization mass spectrometry (SVUV-PIMS). Five literature models were selected to reproduce the experimental data and analyze the reaction kinetics of indene. The experimental and predicted results illustrate that an indenyl radical is the dominant decomposition intermediate and also the main contributor to the further growth of aromatic rings in the pyrolysis of indene. The indene consumption process needs further precise characterization, especially the subsequent dissociation reactions of indanyl and indenyl radicals. A self-recombination reaction of the indenyl radical and the combination reactions between indenyl and other radicals are found to be necessary for the efficient formation of large PAHs. The absence of these pathways leads to the underprediction of experimental measurements. In contrast, literature models adopting indenyl global reactions for PAH formation generally overestimate the system reactivity. Proper radical combination pathways proposed in a future model should consider not only the PAH formation efficiency but also its impact on system reactivity.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...