Unraveling the effect of B-site antisite defects on the electronic and magnetic properties of the quadruple perovskite CaCu3Fe2Nb2O12†
Abstract
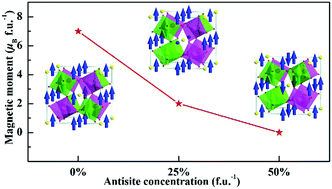
The atomic-scale degree of B/B′ alternate cationic disorder is known to significantly influence the macroscopic properties of the quadruple perovskites AA3′B2B2′O12; however, the nature of this disorder has rarely been critically studied. Herein, the effect of B-site cationic arrangement on the electronic and magnetic properties of the quadruple perovskite CaCu3Fe2Nb2O12 was systemically investigated using the first-principles calculations. The results demonstrate that the B-site ordered CaCu3Fe2Nb2O12 is a ferrimagnetic insulator with antiferromagnetic coupling between the A′-site Cu and B-site Fe. The calculated total magnetic moment is 7.00 μB f.u.−1, which is apparently larger than the experimentally measured saturation magnetization because of different degrees of the B-site disorder. Furthermore, the electronic structures illustrate that the magnetic moments sharply decrease with an increase in the B-site antisite defects, i.e., the total magnetic moments obviously reduce with an increase in the B-site Fe/Nb disorder, and ultimately, no magnetism is observed. Interestingly, the B-site antisite defects not only introduce Fe–Fe antiferromagnetic coupling, but also induce the antiferromagnetic arrangement of Cu spins in the totally disordered structure. Cu–Fe and Fe–Fe magnetic coupling competition is coupled with antisite defects, and finally, Fe–Fe antiferromagnetic coupling turns into the dominating spin coupling in the disordered CaCu3Fe2Nb2O12. Moreover, the B-site antisite defects do not alter the insulator nature of the perovskite despite the significantly narrowed band gap. Our study opens up a novel avenue for the straightforward understanding of the effect of cationic ordering on the electronic and magnetic properties of quadruple perovskites and offers an additional opportunity for tailoring their characteristics.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...