A heterometallic D–A hybrid heterostructural framework with enhanced visible-light photocatalytic properties†
Abstract
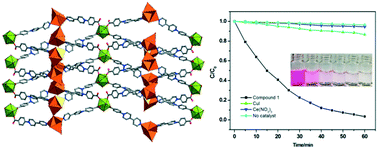
The ternary combination of CuI, lanthanide cations and electron-deficient viologen based organic tectons led to a donor–acceptor (D–A) hybrid heterostructural framework with a narrow energy gap. Thanks to the electron transfer between inorganic donors (cuprous iodide clusters) and organic acceptors (viologen based tectons), this unique hybrid framework exhibits enhanced photocatalytic activities towards the degradation of rhodamine B (RhB) in comparison with those of lanthanide cations and bulk CuI.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...