Heteroepitaxy of perovskite (111) SrTiO3 on wurtzite (0002) GaN using an artificial interface lattice design
Abstract
Rational interface lattice design is the key issue for high quality integration of functional SrTiO3 (STO) oxide on a GaN semiconductor. Based on the heteroepitaxy design principle for minimizing lattice mismatch at the interface, by inserting novel designed hexagonal Ti and spinel MgAl2O4 (MAO) buffer layers, epitaxial integration of the perovskite (111) STO onto wurtzite (0002) GaN was realized using pulsed laser deposition respectively. The epitaxial relationship was resolved to be (111)[1![[1 with combining macron]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_0031_0304.gif) 0] STO//(0002)[11
0] STO//(0002)[11![[2 with combining macron]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_0032_0304.gif) 0] Ti//(0002)[11
0] Ti//(0002)[11![[2 with combining macron]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_0032_0304.gif) 0] GaN and (111)[1
0] GaN and (111)[1![[1 with combining macron]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_0031_0304.gif) 0] STO//(111)[1
0] STO//(111)[1![[1 with combining macron]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_0031_0304.gif) 0] MAO//(0002)[11
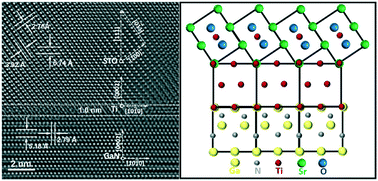
0] MAO//(0002)[11![[2 with combining macron]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_0032_0304.gif) 0] GaN, respectively. Insertion of the ultrathin Ti and MAO buffer layers could reduce lattice mismatch at the STO/GaN interface from +13.3% to +6.5% and +3.3% respectively, thus inducing the epitaxial growth of STO. However, compared to STO with a three-dimensional growth mode on an MAO buffered GaN, STO on GaN with a designed Ti buffer layer displays a dense microstructure, flat surface and great interfacial state. By analyzing the out-of-plane atomic epitaxial matching model of STO/Ti/GaN, high quality integration of STO could originate from the release of the lattice mismatch strain by lattice distortion of the two unit-cell Ti buffer layer, and the low interfacial energy owing to the common Ti atom site and Ti–O at the STO/Ti interface.
0] GaN, respectively. Insertion of the ultrathin Ti and MAO buffer layers could reduce lattice mismatch at the STO/GaN interface from +13.3% to +6.5% and +3.3% respectively, thus inducing the epitaxial growth of STO. However, compared to STO with a three-dimensional growth mode on an MAO buffered GaN, STO on GaN with a designed Ti buffer layer displays a dense microstructure, flat surface and great interfacial state. By analyzing the out-of-plane atomic epitaxial matching model of STO/Ti/GaN, high quality integration of STO could originate from the release of the lattice mismatch strain by lattice distortion of the two unit-cell Ti buffer layer, and the low interfacial energy owing to the common Ti atom site and Ti–O at the STO/Ti interface.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...