Porous Co3O4 nanoplates as an efficient electromaterial for non-enzymatic glucose sensing†
Abstract
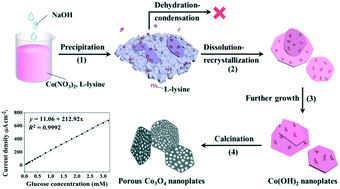
Porous Co3O4 nanoplates constructed by loosely interconnected nanoparticles were synthesized via an L-lysine assisted hydrothermal treatment and subsequent thermal annealing. The hydrothermal conditions of reaction time, reaction temperature and reactant concentrations were investigated in detail. The results suggested that the high affinity of L-lysine could effectively control the redissolution–recrystallization and even restrict the dehydration–condensation reaction of the Co(OH)2 precursor, and thus played the key role for the preparation of the resulting porous Co3O4 nanoplates. Cyclic voltammetry and amperometric methods were used to evaluate the electrochemical performance of the resulting porous Co3O4 nanoplates toward glucose sensing in an alkaline medium. The sensors constructed by the porous Co3O4 nanoplates exhibited a fast response time (within 5 s), a detection limit of 2.7 μM, a sensitivity of 212.92 μA cm−2 mM−1, a linear range from 0.05 mM to 3.2 mM and good stability at a low applied potential (0.38 V vs. Ag/AgCl), suggesting its high performance towards non-enzymatic glucose sensing.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...