Tuning the interpenetration of metal–organic frameworks through changing ligand functionality: effect on gas adsorption properties†
Abstract
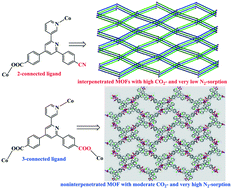
Among metal–organic frameworks (MOFs), the interpenetrated MOFs commonly affect the gas adsorption properties. Herein, a cyano-containing 2-connected ligand, 4-(6-(4-cyanophenyl)-[2,3′-bipyridin]-4-yl)benzoic acid (HL1), was used to construct two novel MOFs ([Co(L1)2] and [Zn(L1)2]), and as a result, two two-fold interpenetrated MOFs were expectantly obtained. Both interpenetrated MOFs possess quasi-hexagonal channels and reveal good CO2 gas adsorption capacities at 273 K, attributable to the nitrile groups in the frameworks of MOFs. In contrast to CO2, both interpenetrated MOFs only have very low N2 gas adsorption capacities at 77 K, suggesting potential application in gas separation. More interestingly, when simple modification of the ligand functional group (from the cyano group to the carboxyl group), a new non-interpenetrated MOF ([Co2(L2)2(H2O)]) with rugby-like channels is constructed by using 3-connected 4,4′-([2,3′-bipyridine]-4,6-diyl) dibenzoic acid (H2L2), which is ascribed to the change in ligand functionality (from the cyano group to the carboxyl group). Significantly, this non-interpenetrated MOF reveals much high N2 gas adsorption capacity at 77 K, and moderate CO2 gas adsorption capacity at 273 K owing to the absence of the nitrile groups in the MOF. Furthermore, the magnetic properties of two Co-based MOFs and photoluminescence of three MOFs have also been investigated. The present work provides a promising approach to design and construct interpenetrated/non-interpenetrated MOFs by changing ligand functionality and to tune gas adsorption properties.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...