Suppressing the compositional non-uniformity of AlGaN grown on a HVPE-AlN template with large macro-steps
Abstract
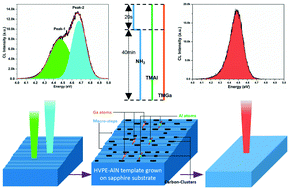
AlGaN is a promising material for ultraviolet optoelectronic and microelectronic devices. In this report, we investigated the influences of metallization pretreatment on the strain, morphology and optical properties of AlGaN grown on HVPE-AlN. The results indicated that the pretreatment could effectively alleviate the compressive strain from HVPE-AlN and thus lower the Al-content in AlGaN. The composition pulling effect was considered to be responsible for the Al-content reduction. On the other hand, the pretreatment could help to improve the surface morphology of AlGaN, which was attributed to the growth mode transition involved in the pretreatment. Besides, the optical measurements revealed that the AlGaN directly grown on HVPE-AlN exhibited distinct compositional non-uniformity and the reasons were the macro-steps in the surface of HVPE-AlN and the mobility discrepancy of Al and Ga atoms. The pretreatment could eliminate such non-uniformity effectively. The carbon clusters formed by metal–organic decomposition during the pretreatment were believed to be responsible for the improvement. The localized excitonic characteristics were also studied. It was found that the localized excitonic states were abundant and energy transport processes were complex in AlGaN directly grown on HVPE-AlN, which would result in undesired light emissions. The pretreatment was proved to be effective in optimizing the localized excitonic characteristics, which may be attributed to the alleviation of Al-content fluctuation by the pretreatment. These results can not only provide a deeper understanding of AlGaN epitaxy, but also offer an approach to optimize the properties of the AlGaN materials.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...