Study on a co-doped CdZnTe crystal containing Yb and In†
Abstract
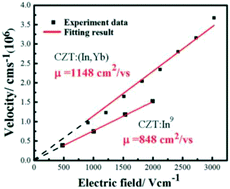
The influence of ytterbium and indium on a co-doped CdZnTe (CZT:(In,Yb)) crystal grown using the vertical Bridgman method was investigated. A new energy level, mainly derived from [YBCd]+, was identified from the photoluminescence (PL) spectra. The trap density of Cd vacancies was obviously reduced along with an increased number of tellurium antisites according to thermally stimulated current (TSC) measurements. A variation in the intensity ratio for the A0X/D0X peak was observed in the PL spectra compared with an indium doped CdZnTe (CZT:In) crystal. Time-of-flight (TOF) results showed that the electron mobility was determined to be 1148 cm2 Vs−1, which is about 26% higher than that of CZT:In. The major cause was considered to be electrical compensation and the gettering process, where the concentrations of Cd vacancies and acceptor impurities were reduced, leading to an enhancement in the mobility.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...