Epitaxial growth of single-crystalline-film scintillators based on Tb3+-doped and Tb3+–Ce3+-codoped Gd1–xLuxAlO3 (x = 0–1) mixed perovskites
Abstract
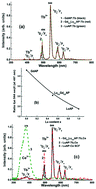
The paper is dedicated to the development of scintillating screens for microimaging applications based on the single crystalline films (SCFs) of singly Tb3+ and doubly Tb3+–Ce3+ doped Gd1–xLuxAlO3 (x = 0–1) mixed perovskites grown onto YAlO3 (YAP) substrates using the liquid phase epitaxy (LPE) method. The cation engineering in Gd1–xLuxAlO3 (x = 0–1) solid solution enabled an improvement of the K-edge of X-ray absorption of SCF scintillators in the 50–63 keV energy range. The structural quality of the grown films was studied using X-ray diffraction and scanning electron microscopy. The optical properties of the Tb3+-doped and Tb3+–Ce3+-codoped Gd1–xLuxAlO3 (x = 0–1) SCFs were investigated by conventional spectroscopic methods, such as absorption, cathodoluminescence (CL), photoluminescence, the light yield of CL, and radioluminescence (RL) measurements under e-beam and α-particle excitation, respectively. Effective Gd3+ → Tb3+ and Gd3+ → Ce3+ → Tb3+ energy transfer processes were observed in Gd1–xLuxAlO3:Tb and Gd1–xLuxAlO3:Tb,Ce SCFs, respectively, explaining the increased efficiency of the Tb3+ luminescence in these perovskite hosts. We found that the highest efficiencies in terms of CL and RL were observed in the doubly Tb3+–Ce3+-doped Gd0.5Lu0.5AlO3 SCFs.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...