Self-assembly of fluoride-encapsulated polyhedral oligomeric silsesquioxane (POSS) nanocrystals†
Abstract
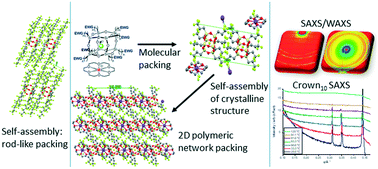
The self-assembly and crystal packing of a unique series of nanocrystalline fluoride ion-encapsulated polyhedral oligomeric silsesquioxane (F-POSS) compounds, with substituted electron-withdrawing group (EWG) perfluorinated alkyl chain arms of varying lengths, were investigated. The fluorine-encapsulated T8[(CH2)n-EWG]8F−-18-crown-6-ether-M+ and T8[(CH2)n-EWG]8F−-tetrabutyl ammonium TBA+ compounds with fluorinated alkyl chain arms were synthesized and subsequently analyzed using differential scanning calorimetry (DSC), thermogravimetric analysis (TGA) and simultaneous small- and wide-angle X-ray scattering (SAXS/WAXS) techniques. DSC and TGA of the compounds showed that the melting temperatures occurred below 100 °C and the compounds were thermally stable above their melting temperatures. SAXS/WAXS data probed the crystalline structure and self-assembly of the nanocrystalline compounds. At ambient temperatures, the crystalline structures of the compounds were seen to be complex with triclinic unit cells. On cooling from the melt, the self-assembly of the compounds with shorter fluorinated alkyl chain arms is dominated by the ionic attraction between the cages such that the arms form a disordered state that only reorder on standing. In contrast, the self-assembly of the compounds with longer fluorinated alkyl chain arms is dominated by the alignment of the arms into rod-like morphologies such that a fully ordered solid is formed from the melt. Electrical characterization has revealed that the POSS cages exhibited an insulating behavior. The POSS cages with or without fluoride ion encapsulation had similar AC conductivities but cages without fluoride ion encapsulation have the highest relative permittivity. The results show that due to the inorganic–organic-ionic nature of the F-POSS ion encapsulated compounds and nanocrystalline self-assembly, they have great potential as interfacial compatibilizers enhancing the miscibility of polymer composites and aiding interactions between polar and non-polar solvents as ionic liquids.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...