Late-stage difluoromethylation leading to a self-immobilizing fluorogenic probe for the visualization of enzyme activities in live cells†
Abstract
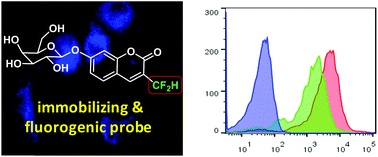
Reported herein is a novel p-quinone methide-based self-immobilizing fluorogenic probe for the visualization of β-galactosidase activities in live cells. This easily prepared imaging reagent massively increases the fluorescence intensity and covalently links to the activation site with high efficiency upon enzymatic trigger.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...