Reaction-based indicator displacement assay (RIA) for the development of a triggered release system capable of biofilm inhibition†
Abstract
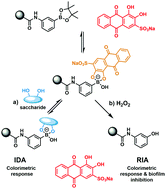
Here, a reaction-based indicator displacement hydrogel assay (RIA) was developed for the detection of hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) via the oxidative release of the optical reporter Alizarin Red S (ARS). In the presence of H2O2, the RIA system displayed potent biofilm inhibition for Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA), as shown through an in vitro assay quantifying antimicrobial efficacy. This work demonstrated the potential of H2O2-responsive hydrogels containing a covalently bound diol-based drug for controlled drug release.
- This article is part of the themed collection: The Mechanics of Supramolecular Chemistry


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...