Condensates of short peptides and ATP for the temporal regulation of cytochrome c activity†
Abstract
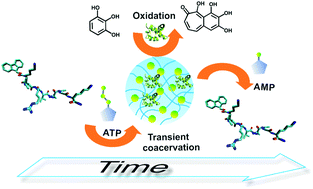
Herein, we report the generation of simple condensates of short peptides with ATP, which are spatiotemporally formed under dissipative conditions created in presence of ATP-ase. These coacervates could imbibe cytochrome c and temporally modulate a redox reaction catalyzed by the entrapped protein, thus mimicking the advanced functional machinery of transient intercellular membraneless condensates of large proteins and RNA.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...