Ti3C2/BiVO4 Schottky junction as a signal indicator for ultrasensitive photoelectrochemical detection of VEGF165†
Abstract
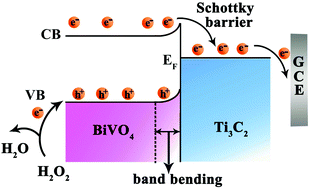
A “signal-on” photoelectrochemical (PEC) biosensor was developed for ultrasensitive detection of vascular endothelial growth factor 165 (VEGF165) based on a Ti3C2/BiVO4 Schottky junction, which was a novel sensitized structure with excellent photovoltaic performance, prominent film-forming ability and stability. The generation of a built-in electric field by the Ti3C2/BiVO4 Schottky junction efficiently suppressed the combination of photogenerated electron–hole pairs and enhanced the photocurrent, providing a high initial photocurrent signal for the construction of a photoelectrochemical (PEC) biosensor.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...