Positron emission tomography probes targeting bromodomain and extra-terminal (BET) domains to enable in vivo neuroepigenetic imaging†
Abstract
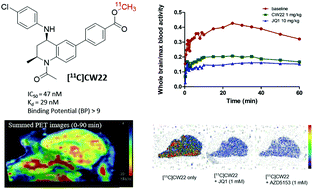
Here, we report the development of novel PET radiotracer ([11C]CW22) of BET proteins. In vivo imaging results in rodents and nonhuman primates (NHP) demonstrate that [11C]CW22 has excellent brain uptake, good specificity, good selectivity, suitable metabolism, appropriate kinetics and distribution in the brain. Our studies demonstrated that [11C]CW22 exhibits ideal properties as a PET imaging probe of BET proteins for further validation.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...